Cooling Fan Technology by SANYO DENKI AMERICA
This site is part of SANYO DENKI’s official cooling engineering knowledge base.
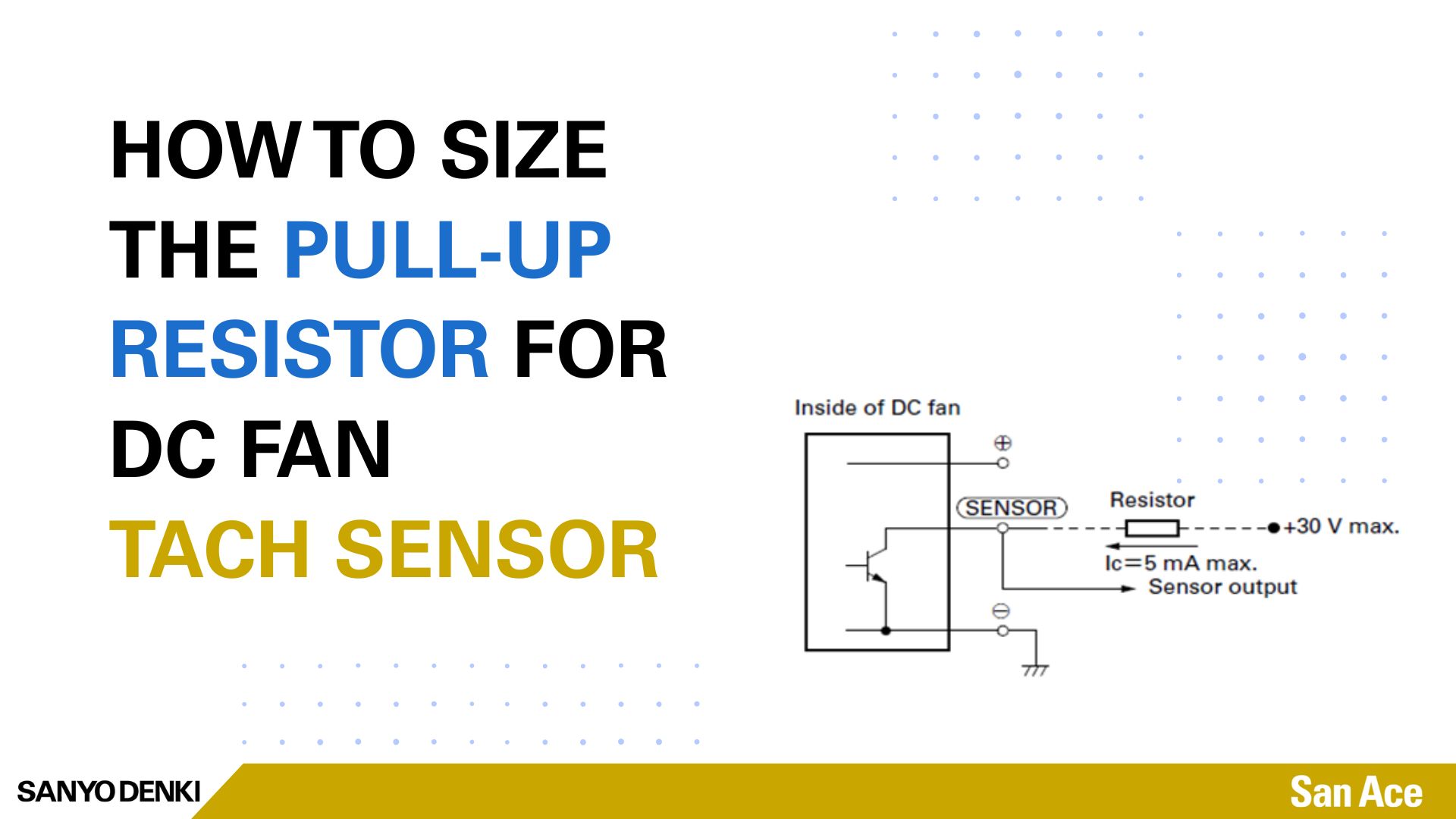
The pulse tach output sensor from our DC fans provides real-time RPM measurements and monitors the health of the fan. It helps determine when the fan’s service life is approaching its end, as well as detecting any abnormalities —making it a valuable tool for scheduling maintenance.
See related article: An Overlooked but Useful Benefit of the Pulse Tach Sensor
We often receive questions from customers who are starting new designs, particularly around how to measure the pulse tach output. This article explains what to consider when designing a circuitry to properly read this output.
Note that, unlike the PWM Input which has an internal Pull-Up resistor (see article: Get to know Protection Features in a Sanyo Denki DC Fan ) the pulse tach output does not have an internal pull-up resistor. It must be added externally by the customer, please refer to the schematic below for proper setup.
Setup


For example: 5mA Max
When choosing an external pull-up resistor, make sure Ic (collector current) does not exceed 5mA—going above this will damage the fan.
Use the Ohm’s Law formula to determine the appropriate resistor:
R = V / I, or specifically, Rpu = VCE / IC
For example:
Common standard values like 3.3kΩ, 3.6kΩ, or 4.7kΩ can also be used. These values (with a VCE of 12V) result in the following collector currents which are all below the 5mA maximum limit:
With the correct pull-up resistor in place, you can now measure the pulse tach output. You should see two pulses for every impeller rotation, as shown in the waveform diagram below.

To properly use the pulse tach output sensor:
Failing to do this may result in permanent damage to the fan.
Need Help?
Contact your local SANYO DENKI representative or sales engineers if you have further questions.
Written by Gary Masessa
SANYO DENKI has been a trusted provider of cooling solutions for various industries, with fans being a crucial component in many advanced devices. Contact us for a quote, or to discuss your device's customization requirements.
Our experienced application engineers and field engineers will provide support on the customization or any other technical support for your equipment. Contact our representatives or distributors to start discussing your next project.
Contact Us